 |
OptiLayer allows you to specify targets for cases when your spectral characteristic \(S(\lambda)\) should satisfy the following conditions:
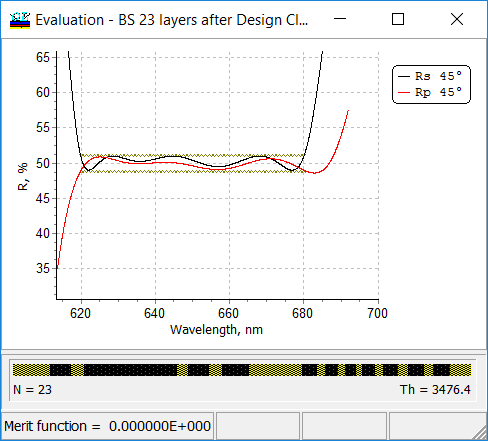
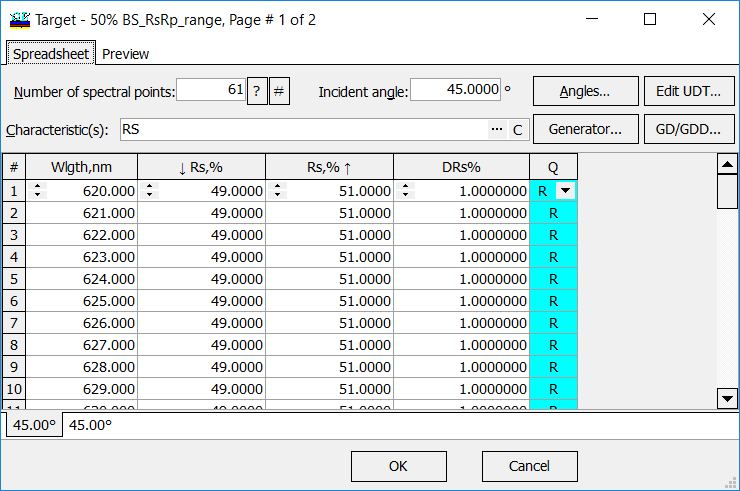
\[ S(\lambda_j)\ge a_j, \] \[ S(\lambda_j)\le b_j, \] \[ a_j\le S(\lambda_j)\le b_j \] Example (left panel). Beamplitter design satisfies range target conditions: \[ 49\%\le R(\lambda_j)\le 51\%, \lambda_j=620+(j-1) \]
|
| Design targets (and therefore a merit function) can be modified using qualifiers A, B or R.
A corresponds to the Bypass Above option. It means that OptiLayer bypasses the target when the corresponding characteristic is greater than a target value. B corresponds to the Bypass Below option. It means that OptiLayer bypasses the target when the corresponding characteristic is less than a target value. R corresponds to the Range option. It means that OptiLayer bypasses the target when the corresponding characteristic belongs to a given segment (see right panel). An empty qualifier (blank) corresponds to a conventional target. |
 |
OptiLayer provides user-friendly interface and a variety of examples allowing even a beginner to effectively start to design and characterize optical coatings. Read more…
Comprehensive manual in PDF format and e-mail support help you at each step of your work with OptiLayer.
If you are already an experienced user, OptiLayer gives your almost unlimited opportunities in solving all problems arising in design-production chain. Visit our publications page.
Look our video examples at YouTube
OptiLayer videos are available here:
Overview of Design/Analysis options of OptiLayer and overview of Characterization/Reverse Engineering options.
The videos were presented at the joint Agilent/OptiLayer webinar.
