| The Quasi-Random Errors mode of the program combines the features of the Systematic Errors and Random Errors modes. It incorporates the sophisticated mathematical algorithm based on the most advanced ideas of the theory of inverse problems (so-called ideas of the regularization of the inverse problem solution).
Quasi-Random Errors mode allows you to take into account a priori information about levels of errors in layer thicknesses. Example: reverse engineering of broadband anti-reflection coating produced with the help of very accurate time monitoring. See the details in our publications.
|
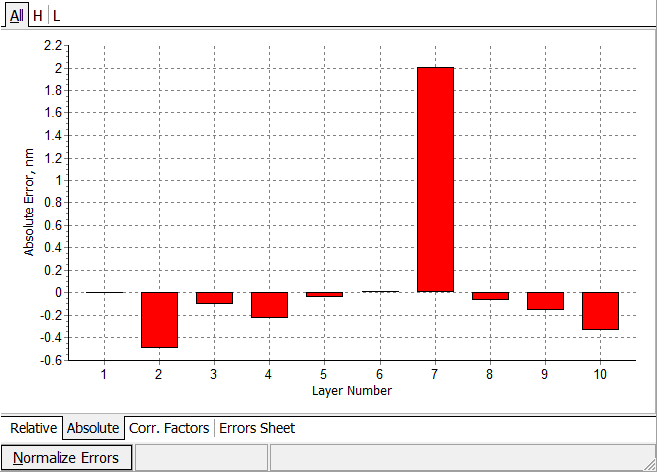
Absolute errors in layer thicknesses estimated using Quasi Random algorithm with a priori information about smallness of the errors. |
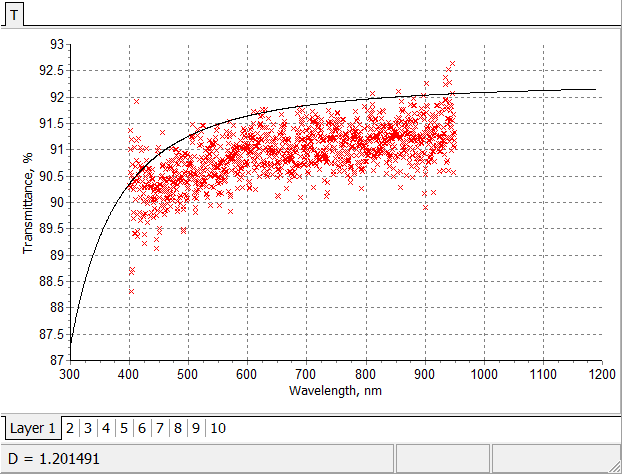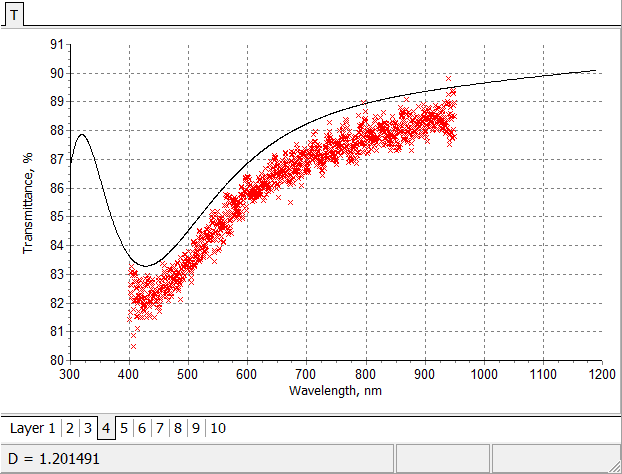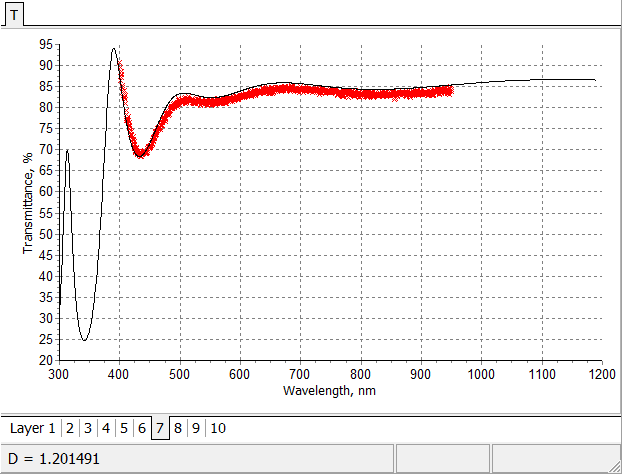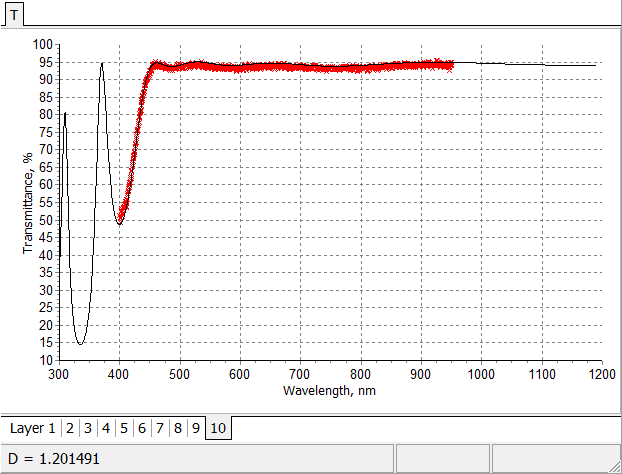
Initial fitting of multiscan in-situ transmittance data by theoretical transmittance of 10-layer anti-reflection coating. |
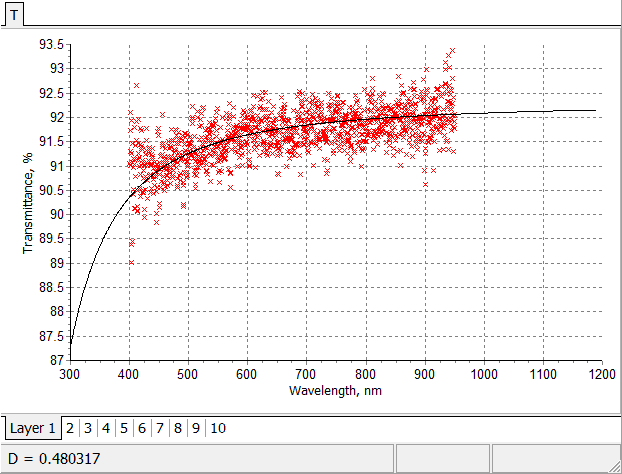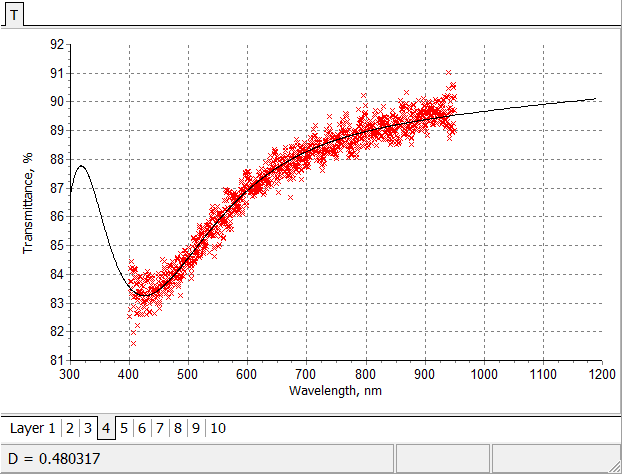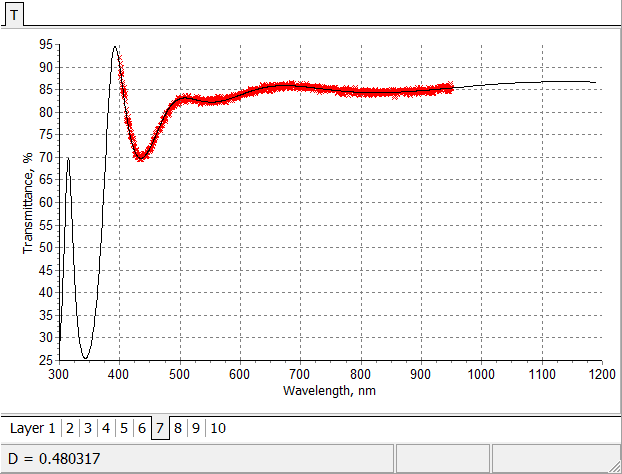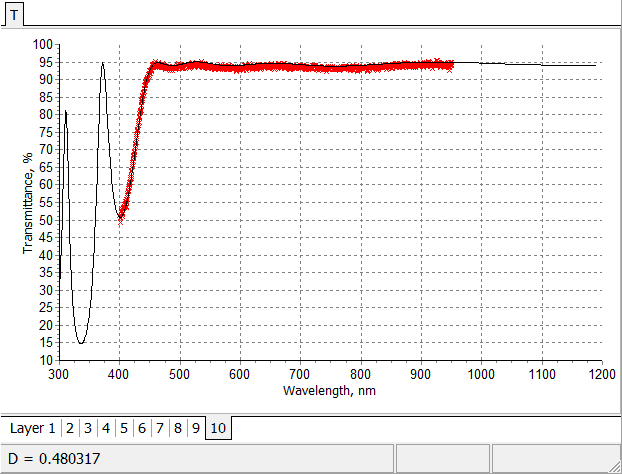
Final fitting of multiscan in-situ transmittance data by model transmittance. |
Application of this mode to reverse engineering problems has been demonstrated in our publications:
|
|
OptiLayer provides user-friendly interface and a variety of examples allowing even a beginner to effectively start to design and characterize optical coatings. Read more…
Comprehensive manual in PDF format and e-mail support help you at each step of your work with OptiLayer.
If you are already an experienced user, OptiLayer gives your almost unlimited opportunities in solving all problems arising in design-production chain. Visit our publications page.
Look our video examples at YouTube
OptiLayer videos are available here:
Overview of Design/Analysis options of OptiLayer and overview of Characterization/Reverse Engineering options.
The videos were presented at the joint Agilent/OptiLayer webinar.
